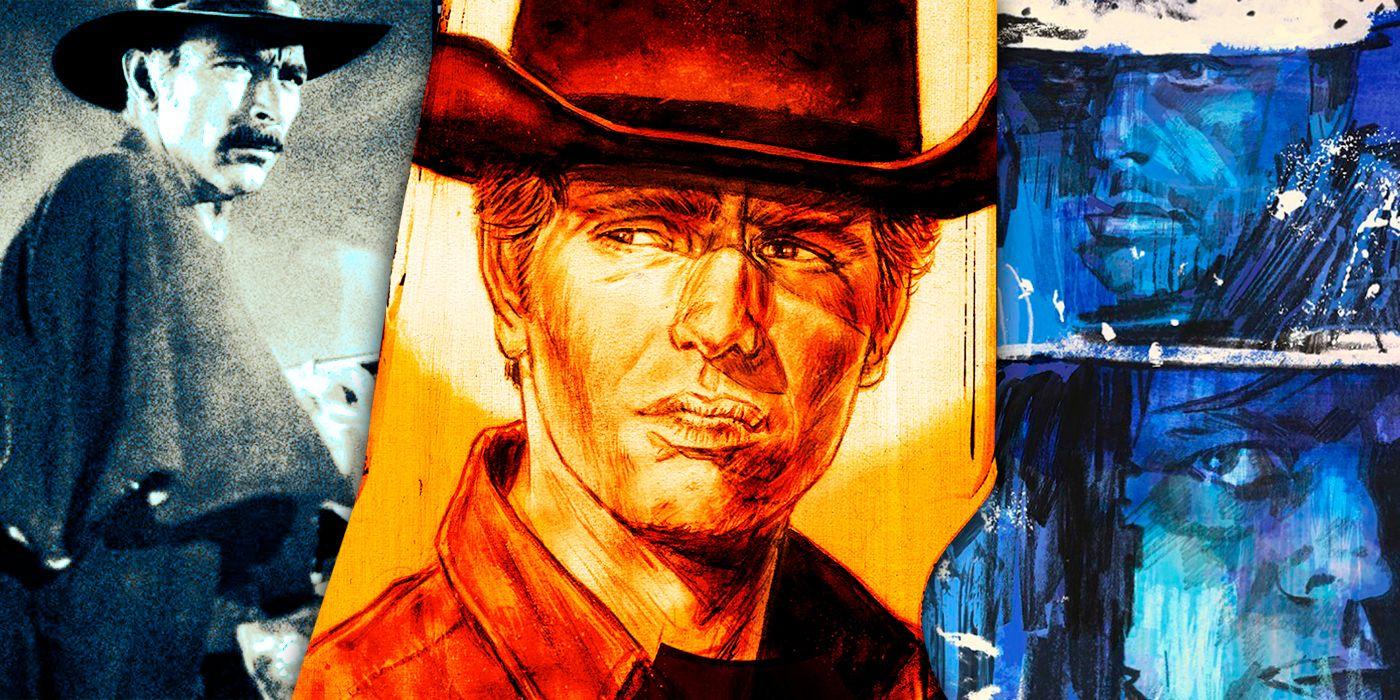
The Western film genre is defined by wide-open landscapes, solitary antiheroes, tense standoffs, and stark morality. Yet, few films have so thoroughly reshaped and embodied the genre as The Good, the Bad and the Ugly (1966). Directed by Sergio Leone and powered by Ennio Morricone’s iconic score, this film has not only achieved cult status but redefined the very tenets of Western storytelling for generations worldwide. Examining its narrative architecture, aesthetic techniques, cultural influence, and ongoing legacy reveals why it is often considered the ultimate Western.
A Groundbreaking Method for Narrative Creation
At its heart, the movie’s brilliance stems from Sergio Leone’s audacious challenge to conventional character molds. In this narrative, the distinctions between good and evil are masterfully obscured. The three main figures—Blondie (the Good), Angel Eyes (the Bad), and Tuco (the Ugly)—do not merely stand as stark moral contrasts, but rather as intricate, imperfect, and unpredictable personalities. None of them personify the archetypal virtuous cowboy or the unequivocally wicked outlaw seen in previous Westerns. Instead, each character is driven by their primal urge to survive, their avarice, and their distinct personal principles.
Leone crafts the storyline around a quest for hidden riches amidst the American Civil War, positioning the broader conflict as a setting rather than the primary focus. This approach allows the filmmaker to highlight the individual paths and evolutions of the main figures. The story intricately blends their drives and loyalties, culminating in an iconic three-way confrontation—a scene that has since been emulated countless times in film.
Visual Narratives and Memorable Filmmaking
Leone’s visual approach was groundbreaking for his era. The filmmaker’s technique of contrasting intense close-ups with expansive landscape panoramas generates a distinctive experiential tension within the movie. Cinematographer Tonino Delli Colli utilizes natural illumination to highlight the dust, perspiration, and ruggedness etched onto every character’s face, thereby boosting realism and simultaneously fostering a mythic quality.
Perhaps the movie’s most renowned visual segment is its finale at Sad Hill Cemetery. With swift cuts, changing viewpoints, and an agonizingly extended quiet, Leone crafts an almost unbearable tension. The interplay of gazes and gestures preceding the gunshots isn’t just dramatic flair; it’s a manifestation of psychological combat, forever reshaping how cinematic shootouts are envisioned.
Reimagining the Auditory Landscape: Ennio Morricone’s Musical Composition
If Leone reimagined the visual lexicon of Westerns, Ennio Morricone fundamentally altered their auditory landscape. The central musical motif of the movie, distinguished by its coyote-esque cries, eerie whistles, and unconventional instrumentation, stands as one of the most iconic scores ever created. This musical composition transcends mere accompaniment; it operates as a driving narrative element, intensifying feelings, delineating personalities, and occasionally even punctuating the unfolding events with a theatrical magnificence.
Morricone’s musical compositions for every principal character—a distinctive whistle for Blondie, a melodic flute for Angel Eyes, and expressive human voices for Tuco—function as aural leitmotifs, deepening their portrayal and inner lives without requiring explanatory conversation. The collaborative effort between the director and the composer in this movie established a lasting standard for the fusion of music and cinematic art.
Moral Ambiguity and the Frontier Myth
Most earlier Western films idolized the frontier, casting the West as a place where good could triumph over evil in a lawless environment. Leone’s film challenges this myth, presenting the Union and Confederate armies not as paragons of virtue or villainy, but as institutions capable of senseless violence and corruption. The futility and chaos of war loom constantly in the background, rendering the treasure hunt both absurd and existential.
The complex morality of the main trio exposes the thin line between good and bad when survival and greed rule. This ambiguity creates a more authentic reflection of the human condition, encouraging audiences to question black-and-white worldviews and the simplistic heroics associated with classic Westerns. The American West in Leone’s hands becomes a metaphor for life’s randomness, danger, and ambiguity.
Influence and Imitation: Setting the Standard
The movie’s impact extends beyond its category. Filmmakers like Quentin Tarantino, Martin Scorsese, and the Coen Brothers have acknowledged its foundational role. The “Mexican standoff”—made famous by the graveyard finale—is now a worldwide cinematic symbol for suspense, deception, and fluctuating authority.
In addition, the movie spawned the “spaghetti Western” subgenre, influencing numerous European and American works that embraced Leone’s distinctive stylistic and thematic elements. The raw authenticity, anti-heroic figures, and intricate moral dilemmas became defining characteristics, ultimately permeating American neo-Westerns, reinterpreted narratives, and even diverse genres, ranging from science fiction to graphic novels.
On a technical front, Leone’s pioneering editing techniques, his utilization of the widescreen Techniscope format, and his groundbreaking integration of musical scores established the foundation for contemporary action filmmaking, shaping the editing pace and audio engineering found in today’s major motion pictures.
A timeless film
Multiple layers of artistry converge in The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. The film’s narrative intricacies, psychological characterization, visual grandeur, and sonic ingenuity form a holistic cinematic experience. Its commentary on violence, morality, and the unpredictability of fate resound even beyond its Western backdrop, offering a timeless meditation on human nature and power.
Through continuous innovation and bold narrative, Leone’s magnum opus resists succumbing to mere nostalgia. Rather, it persists as a foundational work—one that consistently provokes thought, delights, and motivates. With every new generation that rediscovers its gritty confrontations and profound inquiries, the movie stands as more than just a zenith of Western filmmaking; it is a pivotal moment in the universal lexicon of cinema itself.